Slavic Native Faith's Theology And Cosmology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In the Russian and Ukrainian centres of Rodnover theology, the concept of Rod has been emphasised as particularly important. According to the publication ''Izvednik'', a compilation of views on theology and cosmology of various Rodnover organisations, "the rest of the gods are only his faces, noumena, incarnations, hypostases", it is a God similar to the ''
In the Russian and Ukrainian centres of Rodnover theology, the concept of Rod has been emphasised as particularly important. According to the publication ''Izvednik'', a compilation of views on theology and cosmology of various Rodnover organisations, "the rest of the gods are only his faces, noumena, incarnations, hypostases", it is a God similar to the ''
 Cosmologically speaking, Rod is conceived as the spring of universal
Cosmologically speaking, Rod is conceived as the spring of universal
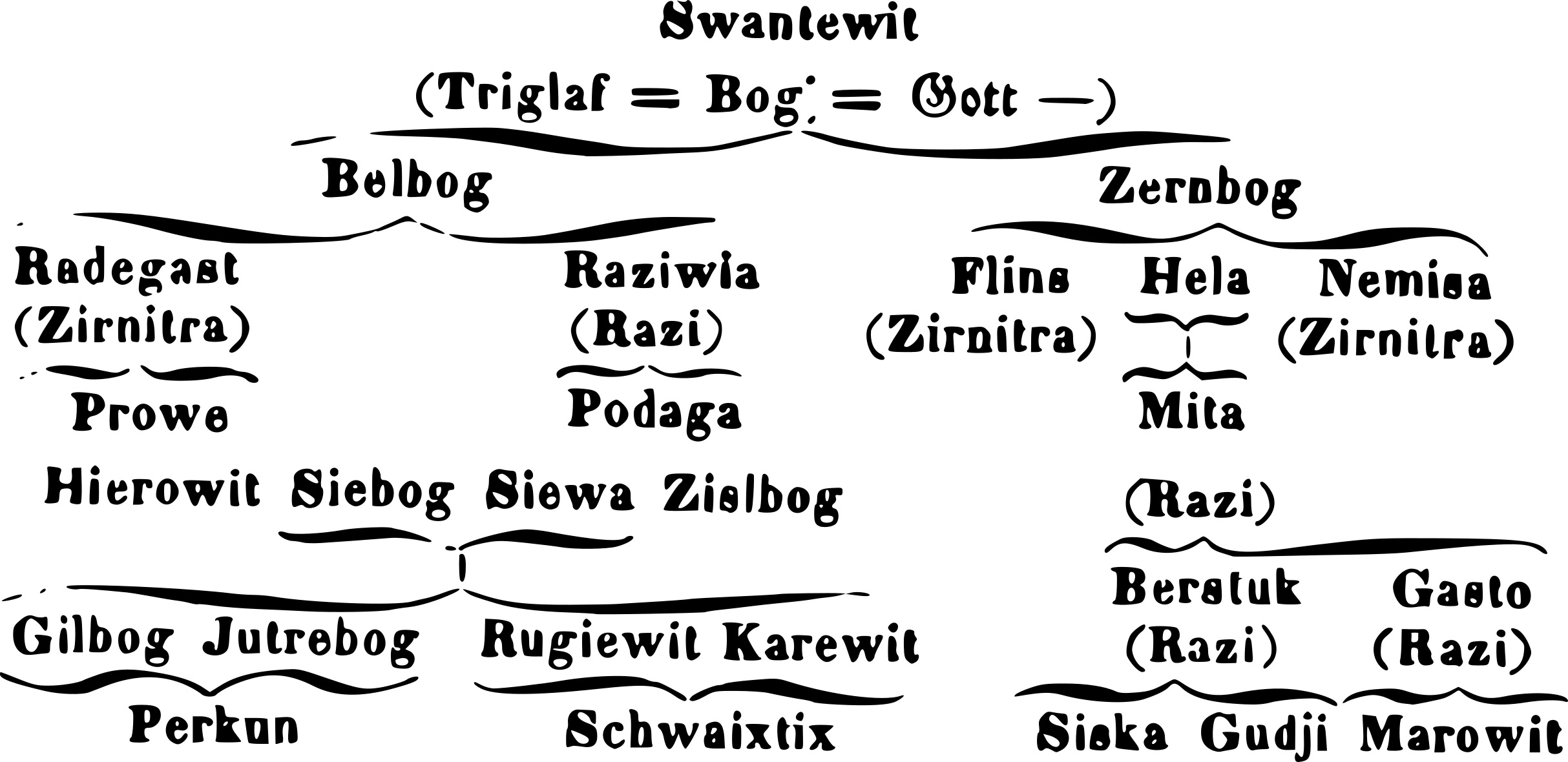 Pantheons of deities are not unified among practitioners of Slavic Native Faith. Different Rodnover groups often have a preference for a particular deity over others. Some Rodnover groups espouse the idea that specific Slavic populations are the progeny of different gods; for instance, groups relying upon the tenth-century manuscript ''The Lay of Igor's Host'' may affirm the idea that Russians are the grandchildren of
Pantheons of deities are not unified among practitioners of Slavic Native Faith. Different Rodnover groups often have a preference for a particular deity over others. Some Rodnover groups espouse the idea that specific Slavic populations are the progeny of different gods; for instance, groups relying upon the tenth-century manuscript ''The Lay of Igor's Host'' may affirm the idea that Russians are the grandchildren of

 In duality, the supreme Rod's luminous aspect (Belobog) manifests ultimately as threefold, ''Triglav'' ("Three-Headed One"). The first of the three persons is the aforementioned Svarog ("Heaven"), and the other two are Svarog's further expressions as Perun ("Thunder") and Svetovid (the "Worldseer", itself four-faced). They correspond to the three dimensions of the
In duality, the supreme Rod's luminous aspect (Belobog) manifests ultimately as threefold, ''Triglav'' ("Three-Headed One"). The first of the three persons is the aforementioned Svarog ("Heaven"), and the other two are Svarog's further expressions as Perun ("Thunder") and Svetovid (the "Worldseer", itself four-faced). They correspond to the three dimensions of the
 Svetovid ("Worldseer", or more accurately "Lord of Power" or "Lord of Holiness", the root *''svet'' defining the "miraculous and beneficial power", or holy power) is the four-faced god of war and light, and "the most complete reflection of the Slavic cosmological conception", the union of the four horizontal directions of space with the three vertical tiers of the cosmos (Heaven, Earth and the underworld), and with the three times.
Svetovid ("Worldseer", or more accurately "Lord of Power" or "Lord of Holiness", the root *''svet'' defining the "miraculous and beneficial power", or holy power) is the four-faced god of war and light, and "the most complete reflection of the Slavic cosmological conception", the union of the four horizontal directions of space with the three vertical tiers of the cosmos (Heaven, Earth and the underworld), and with the three times.

Slavic Native Faith
The Slavic Native Faith, commonly known as Rodnovery
* bg, Родноверие, translit=Rоdnoverie
* bs, Rodnovjerje
* mk, Родноверие, translit=Rodnoverie
* cz, Rodnověří
* hr, Rodnovjerje
* pl, Rodzimowierstwo; Rodzima ...
(Rodnovery) has a theology
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
that is generally monistic
Monism attributes oneness or singleness (Greek: μόνος) to a concept e.g., existence. Various kinds of monism can be distinguished:
* Priority monism states that all existing things go back to a source that is distinct from them; e.g., i ...
, consisting in the vision of a transcendental, supreme God
In monotheism, monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator deity, creator, and principal object of Faith#Religious views, faith.Richard Swinburne, Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Ted Honderich, Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Ox ...
('' Rod'', "Generator") which begets the universe and lives immanentised as the universe itself (pantheism
Pantheism is the belief that reality, the universe and the cosmos are identical with divinity and a supreme supernatural being or entity, pointing to the universe as being an immanent creator deity still expanding and creating, which has ex ...
and panentheism
Panentheism ("all in God", from the Greek language, Greek grc, πᾶν, pân, all, label=none, grc, ἐν, en, in, label=none and grc, Θεός, Theós, God, label=none) is the belief that the Divinity, divine intersects every part of Univers ...
), present in decentralised and autonomous way in all its phenomena, generated by a multiplicity of deities which are independent hypostases, facets, particles or energies of the consciousness and will of the supreme God itself.
A popular dictum is "God is singular and plural". Polytheism
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, the ...
, that is the worship of the gods or spirits, and ancestors, the facets of the supreme Rod generating all phenomena, is an integral part of Rodnovers' beliefs and practices. The universe is described as a "dialectically unfolding manifestation" of the single transcendental beginning, end each subsequent emanation, every deity and entity, is endowed with ontological freedom, spontaneous will to life and co-creation with the supreme law of God (''Prav'', "Right") in the great oneness of which they are part.
The ''swastika
The swastika (卐 or 卍) is an ancient religious and cultural symbol, predominantly in various Eurasian, as well as some African and American cultures, now also widely recognized for its appropriation by the Nazi Party and by neo-Nazis. It ...
''-like ''kolovrat'' (e.g. ) is the symbol of Rodnovery. According to the studies of Boris Rybakov
Boris Alexandrovich Rybakov (Russian: Бори́с Алекса́ндрович Рыбако́в, 3 June 1908, Moscow – 27 December 2001) was a Soviet and Russian historian who personified the anti- Normanist vision of Russian history. He is ...
, whirl and wheel symbols, represent the supreme Rod and its manifestation as the many gods. The vision of Rodnover theology has been variously defined as manifestationism, and rodotheism or genotheism.
Theological stances

Monism and polytheism: Rod and deities
Prior to theirChristianisation
Christianization (American and British English spelling differences#-ise.2C -ize .28-isation.2C -ization.29, or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of ...
, the Slavic peoples were polytheists
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, the ...
, worshipping multiple deities who were regarded as the emanations of a supreme God
In monotheism, monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator deity, creator, and principal object of Faith#Religious views, faith.Richard Swinburne, Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Ted Honderich, Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Ox ...
. According to Helmold
Helmold of Bosau (ca. 1120 – after 1177) was a Saxon historian of the 12th century and a priest at Bosau near Plön. He was a friend of the two bishops of Oldenburg in Holstein, Vicelinus (died 1154) and Gerold (died 1163), who did much to ...
's ''Chronica Slavorum
The ''Chronica Sclavorum'' or ''Chronicle of the Slavs'' is a medieval chronicle which recounts the pre-Christian culture and religion of the Polabian Slavs, written by Helmold (ca. 1120 – after 1177), a Saxon priest and historian. It describe ...
'' (compiled 1168–1169), "obeying the duties assigned to them, he deities
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
have sprung from his he supreme God's
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
blood and enjoy distinction in proportion to their nearness to the god of the gods". Belief in these deities varied according to location and through time, and it was common for the Slavs to adopt deities from neighbouring cultures.
Both in Russia and in Ukraine, modern Rodnovers are divided among those who are monotheists
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford ...
and those who are polytheists; in other words, some emphasise a unitary principle of divinity, while others put emphasis on the distinct gods and goddesses. Some Rodnovers even describe themselves as atheists
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no d ...
, believing that gods are not real entities but rather symbolic and/or archetypal. Monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford ...
and polytheism
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, the ...
are not regarded as mutually exclusive. The shared underpinning is a pantheistic
Pantheism is the belief that reality, the universe and the cosmos are identical with divinity and a supreme supernatural being or entity, pointing to the universe as being an immanent creator deity still expanding and creating, which has ...
view that is holistic
Holism () is the idea that various systems (e.g. physical, biological, social) should be viewed as wholes, not merely as a collection of parts. The term "holism" was coined by Jan Smuts in his 1926 book ''Holism and Evolution''."holism, n." OED Onl ...
in its understanding of the universe. A common interpretation of ancient Slavic beliefs among modern Rodnovers is that of monism
Monism attributes oneness or singleness (Greek: μόνος) to a concept e.g., existence. Various kinds of monism can be distinguished:
* Priority monism states that all existing things go back to a source that is distinct from them; e.g., i ...
, by which the many different gods (polytheism) are seen as manifestations of the single, universal impersonal God—generally identified by the concept of ''Rod'', also known as ''Sud'' ("Judge") and ''Prabog'' ("Pre-God", "First God") among South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hu ...
. The Rodnover movement of Peterburgian Vedism
Peterburgian Vedism (Russian: ) or Peterburgian Rodnovery (), or more broadly Russian Vedism () and Slavic Vedism (), is one of the earliest branches of Rodnovery (Slavic Neopaganism) and one of the most important schools of thought within it, f ...
calls this concept "One God" (Единый Бог, ''Yediny Bog'') or "All God" (Всебог, ''Vsebog''). Rod is generally equated with Odin
Odin (; from non, Óðinn, ) is a widely revered Æsir, god in Germanic paganism. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, v ...
of Germanic Heathenry
Heathenry, also termed Heathenism, contemporary Germanic Paganism, or Germanic Neopaganism, is a modern Pagan religion. Scholars of religious studies classify it as a new religious movement. Developed in Europe during the early 20th centu ...
.
 In the Russian and Ukrainian centres of Rodnover theology, the concept of Rod has been emphasised as particularly important. According to the publication ''Izvednik'', a compilation of views on theology and cosmology of various Rodnover organisations, "the rest of the gods are only his faces, noumena, incarnations, hypostases", it is a God similar to the ''
In the Russian and Ukrainian centres of Rodnover theology, the concept of Rod has been emphasised as particularly important. According to the publication ''Izvednik'', a compilation of views on theology and cosmology of various Rodnover organisations, "the rest of the gods are only his faces, noumena, incarnations, hypostases", it is a God similar to the ''cosmos
The cosmos (, ) is another name for the Universe. Using the word ''cosmos'' implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity.
The cosmos, and understandings of the reasons for its existence and significance, are studied in ...
'' of ancient Greek philosophy in that it is "not the master of the universe, but it itself the universe". While most Rodnovers call it Rod, others call its visible manifestation Svarog
Svarog is a Slavic god of fire and blacksmithing, who was once interpreted as a sky god on the basis of an etymology rejected by modern scholarship. He is mentioned in only one source, the ''Primary Chronicle'', which is problematic in interpret ...
or Nebo ("Heaven"), and still others refer to its triune cosmic manifestation, Triglav ("Three-Headed One"): '' Prav→Yav-Nav'', ''Svarog→Belobog
Chernobog ( "Black God") and Belobog ( "White God") are an alleged pair of Polabian deities. Chernobog appears in the Helmold's '' Chronicle'' as a god of misfortune worshipped by the Wagri and Obodrites, while Belobog is not mentioned – he wa ...
-Chernobog
Chernobog ( "Black God") and Belobog ( "White God") are an alleged pair of Polabian deities. Chernobog appears in the Helmold's '' Chronicle'' as a god of misfortune worshipped by the Wagri and Obodrites, while Belobog is not mentioned – he wa ...
'', ''Svarog→Dazhbog
Dazhbog (russian: Дажьбо́г, Дажбог), alternatively Daždźbok ( be, Даждзьбог), Dažbog, Dazhdbog, Dajbog, Daybog, Dabog, Dazibogu, or Dadzbóg, was one of the major gods of Slavic mythology, most likely a solar deity and ...
- Stribog'', or ''Dub→Snop-Did''. Rod is also "Time" (''Kolo''), scanned by the cycle of the Sun, ad reflected in the turning of the hours, the days, the months, the seasons, and the year.
The root *''rod'' is attested in sources about pre-Christian religion referring to divinity and ancestrality. Mathieu-Colas defines Rod as the "primordial God", but the term also literally means the generative power of the family and "kin", "birth", "origin" and "fate" as well. Rod is the all-pervading, omnipresent spiritual "life force", which also gives life to any community of related entities, as defined by the Russian ''volkhv
A volkhv or volhv (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Волхв; Polish: Wołchw, translatable as wiseman, wizard, sorcerer, magus, i.e. shaman, gothi or magi, mage) is a priest in Slavic paganism, ancient Slavic religions and contemporary Slavic Native ...
''s Veleslav (Ilya Cherkasov) and Dobroslav (Aleksey Dobrovolsky). Its negative form, ''urod'', means anything that is wrenched, deformed, degenerated, monstrous, anything that is "outside" the spiritual community of Rod and bereft of its virtues. Sometimes, the meaning of the word is left deliberately obscure among Rodnovers, allowing for a variety of different interpretations.
Manifestationism
 Cosmologically speaking, Rod is conceived as the spring of universal
Cosmologically speaking, Rod is conceived as the spring of universal emanation Emanation may refer to:
* Emanation (chemistry), a dated name for the chemical element radon
* Emanation From Below, a concept in Slavic religion
* Emanation in the Eastern Orthodox Church, a belief found in Neoplatonism
*Emanation of the state, a l ...
, which articulates in a cosmic hierarchy of gods. When emphasising this monism, Rodnovers may define themselves as ''rodnianin'', "believers in God" (or "in nativity", "in genuinity"). Already the pioneering Ukrainian leader Volodymyr Shaian argued that God manifests as a variety of different deities.
This theological explanation is called "manifestationism" by some contemporary Rodnovers, and implies the idea of a spirit–matter continuum; the different gods, who proceed from the supreme God, generate differing categories of things not as their external creations (as objects), but embodying themselves as these entities. In their view, beings are the progeny of gods; even phenomena such as the thunder are conceived in this way as embodiments of these gods (in this case, Perun
In Slavic mythology, Perun (Cyrillic: Перýн) is the highest god of the pantheon and the god of sky, thunder, lightning, storms, rain, law, war, fertility and oak trees. His other attributes were fire, mountains, wind, iris, eagle, f ...
).
In the wake of this theology, it is common among Slavic Native Faith practitioners to say that "we are not God's slaves, but God's sons", many of them emphasising the ontological freedom of the different subsequent emanations so that the world is viewed as a "dialectical manifestation" of the single transcendental beginning and continuous co-creation of the diversified gods and the entities which they generate. The Russian ''volkhv
A volkhv or volhv (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Волхв; Polish: Wołchw, translatable as wiseman, wizard, sorcerer, magus, i.e. shaman, gothi or magi, mage) is a priest in Slavic paganism, ancient Slavic religions and contemporary Slavic Native ...
'' Velimir (Nikolay Speransky), emphasises a dualistic eternal struggle between white gods and black gods, elder forces of creation and younger forces of destruction; the former collectively represented by Belobog and the latter by Chernobog, also symbolising the spiritual and the material. Such dualism does not represent absolute good and evil
In religion, ethics, philosophy, and psychology "good and evil" is a very common dichotomy. In cultures with Manichaean and Abrahamic religious influence, evil is perceived as the dualistic antagonistic opposite of good, in which good shoul ...
, but the black gods become evil when acting out of agreement with older and stronger white gods.
Clusters of deities
 Pantheons of deities are not unified among practitioners of Slavic Native Faith. Different Rodnover groups often have a preference for a particular deity over others. Some Rodnover groups espouse the idea that specific Slavic populations are the progeny of different gods; for instance, groups relying upon the tenth-century manuscript ''The Lay of Igor's Host'' may affirm the idea that Russians are the grandchildren of
Pantheons of deities are not unified among practitioners of Slavic Native Faith. Different Rodnover groups often have a preference for a particular deity over others. Some Rodnover groups espouse the idea that specific Slavic populations are the progeny of different gods; for instance, groups relying upon the tenth-century manuscript ''The Lay of Igor's Host'' may affirm the idea that Russians are the grandchildren of Dazhbog
Dazhbog (russian: Дажьбо́г, Дажбог), alternatively Daždźbok ( be, Даждзьбог), Dažbog, Dazhdbog, Dajbog, Daybog, Dabog, Dazibogu, or Dadzbóg, was one of the major gods of Slavic mythology, most likely a solar deity and ...
(the "Giving God", "Day God"). The Union of Slavic Rodnover Communities founded and led by Vadim Kazakov recognises a pantheon of over thirty deities emanated by the supreme Rod; these include attested deities from Slavic pre-Christian and folk traditions, Slavicised Hindu deities (such as ''Vyshen'', i.e. Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within t ...
, and ''Intra'', i.e. Indra
Indra (; Sanskrit: इन्द्र) is the king of the devas (god-like deities) and Svarga (heaven) in Hindu mythology. He is associated with the sky, lightning, weather, thunder, storms, rains, river flows, and war. volumes/ref> I ...
), Iranian deities (such as Simargl
Simargl (also Sěmargl, Semargl) or Sěm and Rgel is an East Slavic god or gods, mentioned in two sources. The origin and etymology of this/these figure(s) is the subject of considerable debate. The dominant view is to interpret Simargl as a singl ...
and Khors), deities from the ''Book of Veles
The Book of Veles (also: Veles Book, Vles book, ''Vles kniga'', Vlesbook, Isenbeck's Planks, , , , , , ) is a literary forgery purporting to be a text of ancient Slavic religion and history supposedly written on wooden planks.
It contains reli ...
'' (such as Pchelich), and figures from Slavic folk tales such as the wizard Koschei
Koschei ( rus, Коще́й, r=Koshchey, p=kɐˈɕːej), often given the epithet "the Immortal", or "the Deathless" (russian: Коще́й Бессме́ртный), is an archetypal male antagonist in Russian folklore.
The most common feature of ...
. Rodnovers also worship tutelary deities
A tutelary () (also tutelar) is a deity or a spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of "tutelary" expresses the concept of safety an ...
of specific elements, lands and environments, such as waters, forests and the household. Gods may be subject to functional changes among modern Rodnovers; for instance, the traditional god of livestock and poetry Veles is called upon as the god of literature and communication.
Monotheism
In Ukraine, there has been a debate as to whether the religion should be monotheistic or polytheistic. In keeping with the pre-Christian belief systems of the region, the groups who inherit Volodymyr Shaian's tradition, among others, espouse polytheism. Conversely, Lev Sylenko'sNative Ukrainian National Faith
The Native Ukrainian National Faith ( uk, Рі́дна Украї́нська Націона́льна Ві́ра, ; widely known by the acronym , RUNVira), also called Sylenkoism () or Sylenkianism (), and institutionally also known as the Chur ...
(RUNVira for short, also called "Sylenkoism") regards itself as monotheistic and focuses its worship upon a single God whom they identify by the name Dazhbog, interpreted as the life-giving energy of the cosmos.
Sylenko characterised Dazhbog as "light, endlessness, gravitation, eternity, movement, action, the energy of unconscious and conscious being". Based on this description, Ivakhiv argued that Sylenkoite theology might better be regarded as pantheistic
Pantheism is the belief that reality, the universe and the cosmos are identical with divinity and a supreme supernatural being or entity, pointing to the universe as being an immanent creator deity still expanding and creating, which has ...
or panentheistic
Panentheism ("all in God", from the Greek grc, πᾶν, pân, all, label=none, grc, ἐν, en, in, label=none and grc, Θεός, Theós, God, label=none) is the belief that the divine intersects every part of the universe and also extends bey ...
rather than monotheistic. Sylenko acknowledged that the ancient Slavs were polytheists but believed that a monotheistic view reflected an evolution in human spiritual development and thus should be adopted. A similar view is espoused by Russian Ynglism
Ynglism ( Russian: Инглии́зм; Ynglist runes: ), institutionally the Ancient Russian Ynglist Church of the Orthodox Old Believers–Ynglings (Древнерусская Инглиистическая Церковь Православны� ...
, while another distinctively monotheistic Rodnover movement that has been compared to Sylenkoism is Russian Kandybaism
The Russian Religion (Russian language, Russian: Русская Религия), also termed Russian Vedism (Русский Ведизм), is one of the earliest doctrines of Rodnovery (Slavic Neopaganism) in Russia, founded in 1992 in Saint Pe ...
. Lesiv reported about a Sylenkoite follower who said that "we cannot believe in various forest, field and water spirits today. Yes, our ancestors believed in these things but we should not any longer", as polytheism is regarded as obsolete within the religion. Some polytheist Rodnovers have deemed the view adopted by Sylenko's followers as an inauthentic approach to the religion.
Cosmology

Dual dynamism: Belobog and Chernobog
According to the ''Book of Veles
The Book of Veles (also: Veles Book, Vles book, ''Vles kniga'', Vlesbook, Isenbeck's Planks, , , , , , ) is a literary forgery purporting to be a text of ancient Slavic religion and history supposedly written on wooden planks.
It contains reli ...
'', and to the doctrine accepted by many Rodnover organisations, the supreme Rod begets ''Prav'' (literally "Right" or "Order"; cf. Greek ''Orthotes
Orthotes ( el, ὀρθότης "rightness") is a Greek philosophy concept which means approximately "an eye's correctness". In Plato's philosophy it is said to be the passage from the physical eyes to the eyes of the intellect.
At least this seems ...
'', Sanskrit '' Ṛta'') in primordial undeterminacy (chaos
Chaos or CHAOS may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Fictional elements
* Chaos (''Kinnikuman'')
* Chaos (''Sailor Moon'')
* Chaos (''Sesame Park'')
* Chaos (''Warhammer'')
* Chaos, in ''Fabula Nova Crystallis Final Fantasy''
* Cha ...
), giving rise to the circular pattern of Svarog
Svarog is a Slavic god of fire and blacksmithing, who was once interpreted as a sky god on the basis of an etymology rejected by modern scholarship. He is mentioned in only one source, the ''Primary Chronicle'', which is problematic in interpret ...
("Heaven", "Sky"; cf. Sanskrit ''Svarga
Svarga (), also known as Indraloka and Svargaloka, is the celestial abode of the devas in Hinduism. Svarga is one of the seven higher lokas ( esoteric planes) in Hindu cosmology. Svarga is often translated as heaven, though it is regarded to b ...
''), which constantly multiplies generating new worlds (world-eggs). Prav is Rod itself manifesting as the universe. Prav works by means of a dual dynamism, represented by Belobog ("White God") and Chernobog ("Black God"); described as the "second tier" in the cosmological hierarchy, they are two aspects of "spontaneous division" of the same oneness of Rod, appearing in reality as elder white gods of creation and younger black gods of destruction, the forces of waxing and waning, giving rise to polarities like up and down, bright and dark, masculine and feminine, singular and plural. The younger black gods have always to act in accordance with stronger white gods, otherwise they generate evil. The Belobog–Chernobog duality is also represented on the human plane as the Perun
In Slavic mythology, Perun (Cyrillic: Перýн) is the highest god of the pantheon and the god of sky, thunder, lightning, storms, rain, law, war, fertility and oak trees. His other attributes were fire, mountains, wind, iris, eagle, f ...
– Veles duality, where the former is the principle of martiality and the latter is the principle of mystical philosophy. Man and woman are further symbolised by father Svarog itself and mother Lada.
This supreme polarity is also represented by the relation between Rod and ''Rozanica'', literally the "Generatrix", the mother goddess who expresses herself as the three goddesses who interweave destiny (''Rozanicy'', also known as ''Sudenicy'' among South Slavs, where Rod is also known as Sud, "Judge"). She is also known as ''Raziwia'', ''Rodiwa'' or simply ''Dewa'' ("Goddess"), regarded as the singular goddess of whom all lesser goddesses are manifestations. In kinships, while Rod represents the forefathers from the male side, Rozanica represents the ancestresses from the female side. Through the history of the Slavs, the latter gradually became more prominent than the former, because of the importance of the mother to the newborn child.
The three qualities of reality and the ''axis mundi''
Triglav
cosmos
The cosmos (, ) is another name for the Universe. Using the word ''cosmos'' implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity.
The cosmos, and understandings of the reasons for its existence and significance, are studied in ...
, and to the three qualities of soul, flesh and power. Svarog represents Prav itself and soul, Perun represents ''Yav'' and flesh, and Svetovit represents ''Nav'' and spiritual power. The Triglav is not a combination of gods, but the theological representation of the triadic principle which underlies reality.
According to Shnirelman, this triune vision and associations were codified by Yury P. Mirolyubov and further elaborated by Valery Yemelyanov, both interpreters of the ''Book of Veles''. In olden times, already Ebbo documented that the Triglav was seen as embodying the connection and mediation between Heaven, Earth and the underworld. Adam of Bremen
Adam of Bremen ( la, Adamus Bremensis; german: Adam von Bremen) (before 1050 – 12 October 1081/1085) was a German medieval chronicler. He lived and worked in the second half of the eleventh century. Adam is most famous for his chronicle ''Gesta ...
described the Triglav of Wolin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from th ...
as ''Neptunus triplicis naturae'' (that is to say "Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times ...
of the three natures/generations") attesting the colours that were associated to the three worlds, then further studied by Karel Jaromír Erben
Karel Jaromír Erben (; 7 November 1811 – 21 November 1870) was a Czech folklorist and poet of the mid-19th century, best known for his collection '' Kytice'', which contains poems based on traditional and folkloric themes.
He also wrote ''P ...
: white for Heaven, green for Earth and black for the underworld. Other names of the two manifestations of Svarog are Dazhbog ("Giving God", "Day God") and Svarozhich (the god of fire, literally meaning "Son of Heaven"). According to the studies of Jiří Dynda, the three faces of Triglav are rather Perun in the heavenly plane (instead of Svarog), Svetovid in the centre from which the horizontal four directions unfold, and Veles in the underworld. The netherworld, especially in its dark aspect, is indeed traditionally embodied by Veles, who in this function is the god of waters but also the one who guides athwart them in the function of psychopomp
Psychopomps (from the Greek word , , literally meaning the 'guide of souls') are supernatural creatures, spirits, entities, angels, demons or deities in many religions whose responsibility is to escort newly deceased souls from Earth to the afte ...
(cf. Sanskrit ''Varuna
Varuna (; sa, वरुण, , Malay: ''Baruna'') is a Vedic deity associated initially with the sky, later also with the seas as well as Ṛta (justice) and Satya (truth). He is found in the oldest layer of Vedic literature of Hinduism, such ...
''). Veles is the master of the material world, who magically creates, destroys and synthesises all contradictory tendences; he is associated with the forests and with animals, chiefly the bear, the wolf and the cattle — the Slavic priests themselves, known as ''volkhv
A volkhv or volhv (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Волхв; Polish: Wołchw, translatable as wiseman, wizard, sorcerer, magus, i.e. shaman, gothi or magi, mage) is a priest in Slavic paganism, ancient Slavic religions and contemporary Slavic Native ...
''s (a derivative of ''volk'', "wolf"), are his impersonators.
In his study of Slavic cosmology, Dynda compares this ''axis mundi
In astronomy, axis mundi is the Latin term for the axis of Earth between the celestial poles.
In a geocentric coordinate system, this is the axis of rotation of the celestial sphere.
Consequently, in ancient Greco-Roman astronomy, the '' ...
'' concept to similar ones found in other Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
cultures. He gives weight to the Triglav as a representation of what Georges Dumézil studied as the "Indo-European trifunctional hypothesis
The trifunctional hypothesis of prehistoric Proto-Indo-European society postulates a tripartite ideology ("''idéologie tripartite''") reflected in the existence of three classes or castes— priests, warriors, and commoners (farmers or trades ...
" (holy, martial and economic functions reflected by three human types and social classes). The Triglav also represents the interweaving of the three dimensions of time, metaphorically represented as a three-threaded rope. By Ebbo's words, the Triglav is ''summus deus'', the god representing the "sum" of the three dimensions of reality as a mountain or tree (themselves symbols of the ''axis mundi''). In a more abstract theoretical formulation, Dynda says that the three (Triglav) completes the two by springing out as the middle term between the twosome (Belobog and Chernobog), and in turn the threesome implicates the four (Svetovid) as its own middle term of potentiality. The threefold vertical axle intersecting the fourfold horizontal directions is also mythologically represented as the ninefold world tree
The world tree is a motif present in several religions and mythologies, particularly Indo-European religions, Siberian religions, and Native American religions. The world tree is represented as a colossal tree which supports the heavens, thereb ...
, whose different "worlds" are accessible to those people who have achieved corresponding stages of enlightenment.
Svetovid
Helmold
Helmold of Bosau (ca. 1120 – after 1177) was a Saxon historian of the 12th century and a priest at Bosau near Plön. He was a friend of the two bishops of Oldenburg in Holstein, Vicelinus (died 1154) and Gerold (died 1163), who did much to ...
defined Svetovid as ''deus deorum'' ("god of all gods"); Dynda further defines Svetovid, by Jungian
Analytical psychology ( de , Analytische Psychologie, sometimes translated as analytic psychology and referred to as Jungian analysis) is a term coined by Carl Jung, a Swiss psychiatrist, to describe research into his new "empirical science" ...
words, as a "fourfold (''quaternitas'') potentiality which comes true in threefoldness (''triplicitas'')". His four faces are the masculine Svarog ("Heaven", associated to the north direction and the colour white) and Perun ("Thunder", the west and red), and the feminine Mokosh
Mokosh ( orv, Мóкошь) is a Slavic goddess mentioned in the Primary Chronicle, protector of women's work and women's destiny. She watches over spinning and weaving, shearing of sheep, and protects women in childbirth. Mokosh is the Mother G ...
("Wetness", the east and green) and Lada ("Beauty", the south and black). The four directions and colours also represent the four Slavic lands of original sacred topography. They also represent the spinning of the four seasons.
Ultimately, Svetovid embodies in unity the supreme duality (Belobog and Chernobog) through which Rod manifests itself as Prav, and the axial interconnection of the three times with the four dimensions of present space. In other words, he represents Prav spiritualising Yav as Nav; or Svarog manifesting as spirit (Perun) in the material world governed by Veles. Dynda says that this conception reflects a common Indo-European spiritual vision of the cosmos, the same which was also elaborated in early and medieval Christianity as God who is at the same time creator (father), creature (son) and creating activity (spirit).
Prav, Yav and Nav—Heaven, Earth and humanity

Cosmology of the ''Book of Veles''
According to the ''Book of Veles'', reality has three dimensions, namely the aforementioned ''Prav'', plus ''Yav'' and ''Nav''. The three are identified with different names by different groups. Prav ("Right") itself is the level of the gods, who generate entities according to the supreme order of Rod; gods and the entities that they beget "make up" the great Rod. Yav ("actuality" or "manifestation") is the level of matter and appearance, the here and now in which things appear in light, coalesce, but also dissolve in contingency; Nav ("probability" or "unmanifestation") is the thin world of human ancestors, of spirit, consisting in the memory of the past and the projection of the future, that is to say the continuity of time. Prav, the universal cosmic order otherwise described as the "Law of Heaven", permeates and regulates the other two hypostases. They are also described, respectively, as the world of bright gods, the world of mankind, and the world of dark gods.Genotheism and the worship of ancestors
In her theological commentaries to the ''Book of Veles'', the Ukrainian Rodnover leaderHalyna Lozko
Halyna Lozko ( uk, Галина Сергіївна Лозко) (Yelanets ( uk, Єланець); 3 February 1952 in Mykolaiv Oblast) is Ukrainian ethnologist, theologian and neopagan leader. In 1993 she founded the group Pravoslavia in Kyiv, whi ...
emphasises the cosmological unity of the three planes of Heaven, Earth and humanity between them. She gives a definition of Rodnover theology and cosmology as "genotheism". God, hierarchically manifesting as different hypostases, a multiplicity of gods emerging from the all-pervading force Svarog, is genetically (''rodovid'') linked to humanity. On the human plane God is incarnated by the progenitors/ancestors and the kin lineage, in the Earth. Ethics and morality ultimately stem from this cosmology, as harmony with nature is possible only in the relationship between an ethnic group and its own land. The same vision of a genetic essence of divinity is called "rodotheism" by the Ynglists.
This is also the meaning of the worship of human progenitors, whether the Slavs' and Aryans' great forefather ''Or'' or ''Oryi'', or local forefathers such as ''Dingling'' worshipped by Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea ...
Rodnovers. Divine ancestors are the spirits who generate and hold together kins, they ''are'' the kins themselves. The Russian ''volkhv
A volkhv or volhv (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Волхв; Polish: Wołchw, translatable as wiseman, wizard, sorcerer, magus, i.e. shaman, gothi or magi, mage) is a priest in Slavic paganism, ancient Slavic religions and contemporary Slavic Native ...
'' Dobroslav emphasises the importance of blood heritage, since, according to him, the violation of kinship purity brings about the loss of the relationship with the kin's divine ancestor. The Ukrainian Rodnover and scholar Yury Shylov has developed a theory of God as a spiral "information field" that expresses itself in self-conscious humanity, which comes to full manifestation in the Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
"Saviour" archetype.
See also
*Slavic Native Faith
The Slavic Native Faith, commonly known as Rodnovery
* bg, Родноверие, translit=Rоdnoverie
* bs, Rodnovjerje
* mk, Родноверие, translit=Rodnoverie
* cz, Rodnověří
* hr, Rodnovjerje
* pl, Rodzimowierstwo; Rodzima ...
;Variations
* Anastasian theology
* Bazhovite theology
* Ivanovite theology
* Kandybaite theology
* Levashovite theology
Levashovism is a doctrine and healing system of Rodnovery (Slavic neopaganism) that emerged in Russia, formulated by the physics, physics theorist, occultism, occultist and energy medicine, psychic healer Nikolay Viktorovich Levashov (1961–2012 ...
* Peterburgian Vedic theology
* Sylenkoite theology
* Vseyasvetnik theology
* Ynglist theology
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Theology Slavic neopaganism Modern pagan theology